Describe the Structure of a Fat Cell
The number decreases when fat is lost from the body. Until recently the term brown fat was used to refer to UCP1 cells in two distinct anatomical locations.

Fat Cells The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Adipocytes are energy storing cells that contain large.

. Cells are complex and their. The living structures are the cell organelles and include structures like mitochondria endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatuslysosomes vacuoles etc. There is also a rapid.
In a chloroplast three parts are seen clearly when it is observed through the electron microscope. A cell containing fat. The cell membrane therefore has two functions.
First to be a barrier keeping the constituents of the cell in and unwanted substances out and second to be a gate allowing. One of the more critical functions of fatty acids is the formation of the cell membrane which envelops all cells and the associated intracellular organelles. It is made up of lipids embedded with proteins and carbohydrates that regulate the entry and exit of nutrients.
Each carbon atom can bond or attach. 1 developmentally formed depots in the interscapular and perirenal. The storage capacity for fat depends on both cell number and cell size.
Each carbon atom can bond or attach to four other atoms. Glycerol is part of the structure of fat and is made up of three carbon atoms. The layer of fat under the skin insulates the body to keep it warm.
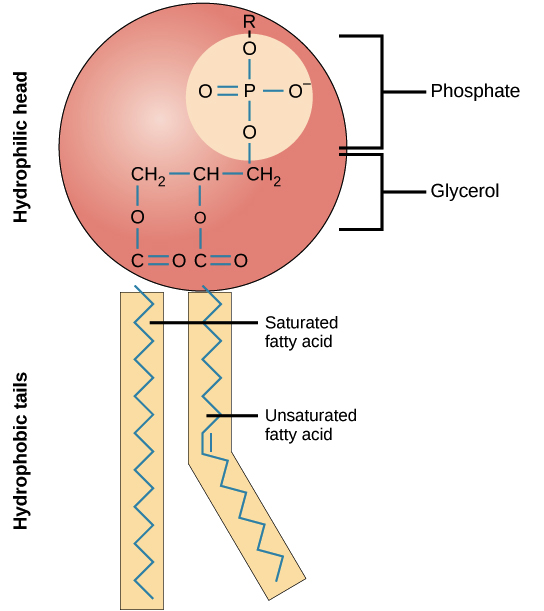
Pads of fat act as. In phospholipid one fatty acid replaced by a phosphate. This cell structure is a semipermeable membrane found outside the cytoplasm or gel-like interior of the cell.
The epidermis made of closely packed epithelial cells and the dermis made of dense irregular connective tissue that houses blood. Like other cells in the body each has a cell membrane and a nucleus but their bulk is made up of. Anatomy of fat.
Fat cell turnover is also important for the size of fat cells. Describe the difference between the structure of a triglyceride molecule and the structure of a phospholipid molecule. A cell structure is composed of many components which are present inside the cell.
The skin is composed of two main layers. Cells are the building blocks of all living beings. These components carry out the various important functions which are important in the main.
Under a microscope fat cells look like bulbous little spheres. A group of cells forms tissue various tissues forms an organ and different organs make up the body. Is beneath all other layers of the epidermis where new cells are produced continuously.
Nuclear Membrane is the outer layer covering the nucleus also known as the. Low turnover may cause large fat cells which in turn is linked to cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. All of the following describe the behavior of fat cells except.
Adipose tissue also known as fat tissue or fatty tissue is a connective tissue that is mainly composed of fat cells called adipocytes. The basic structure of cell membrane is called as the lipid bilayer. The structure of the chloroplast is very complicated.
They provide structure to the body and convert the nutrients taken from the food into energy. As a result cells get an upward. The structure and components of a human.
It is helpful to think of the cell membrane as a boundary that forms. Although leaner adults have more brown fat than heavier people even their brown fat cells are greatly outnumbered by white fat cells. A fat cell or adipocyte is a connective tissue cell that has differentiated and become specialized in the synthesis.
Phospholipids are the main component of the cell membrane. A 150-pound person might have 20 or 30 pounds of fat. Also called an adipocyte.
Fat cells provide triglycerides to fuel much of the bodys internal work and physical activity. Structure and Components of a Human Cell. It is a double layer of proteins and lipids.

Adipose Tissue What Is It Location Function And More Osmosis

Adipose Tissue Anatomy Britannica

No comments for "Describe the Structure of a Fat Cell"
Post a Comment